this post was submitted on 13 Sep 2024
1533 points (99.3% liked)
Science Memes
15009 readers
1702 users here now
Welcome to c/science_memes @ Mander.xyz!
A place for majestic STEMLORD peacocking, as well as memes about the realities of working in a lab.

Rules
- Don't throw mud. Behave like an intellectual and remember the human.
- Keep it rooted (on topic).
- No spam.
- Infographics welcome, get schooled.
This is a science community. We use the Dawkins definition of meme.
Research Committee
Other Mander Communities
Science and Research
Biology and Life Sciences
- !abiogenesis@mander.xyz
- !animal-behavior@mander.xyz
- !anthropology@mander.xyz
- !arachnology@mander.xyz
- !balconygardening@slrpnk.net
- !biodiversity@mander.xyz
- !biology@mander.xyz
- !biophysics@mander.xyz
- !botany@mander.xyz
- !ecology@mander.xyz
- !entomology@mander.xyz
- !fermentation@mander.xyz
- !herpetology@mander.xyz
- !houseplants@mander.xyz
- !medicine@mander.xyz
- !microscopy@mander.xyz
- !mycology@mander.xyz
- !nudibranchs@mander.xyz
- !nutrition@mander.xyz
- !palaeoecology@mander.xyz
- !palaeontology@mander.xyz
- !photosynthesis@mander.xyz
- !plantid@mander.xyz
- !plants@mander.xyz
- !reptiles and amphibians@mander.xyz
Physical Sciences
- !astronomy@mander.xyz
- !chemistry@mander.xyz
- !earthscience@mander.xyz
- !geography@mander.xyz
- !geospatial@mander.xyz
- !nuclear@mander.xyz
- !physics@mander.xyz
- !quantum-computing@mander.xyz
- !spectroscopy@mander.xyz
Humanities and Social Sciences
Practical and Applied Sciences
- !exercise-and sports-science@mander.xyz
- !gardening@mander.xyz
- !self sufficiency@mander.xyz
- !soilscience@slrpnk.net
- !terrariums@mander.xyz
- !timelapse@mander.xyz
Memes
Miscellaneous
founded 2 years ago
MODERATORS
you are viewing a single comment's thread
view the rest of the comments
view the rest of the comments
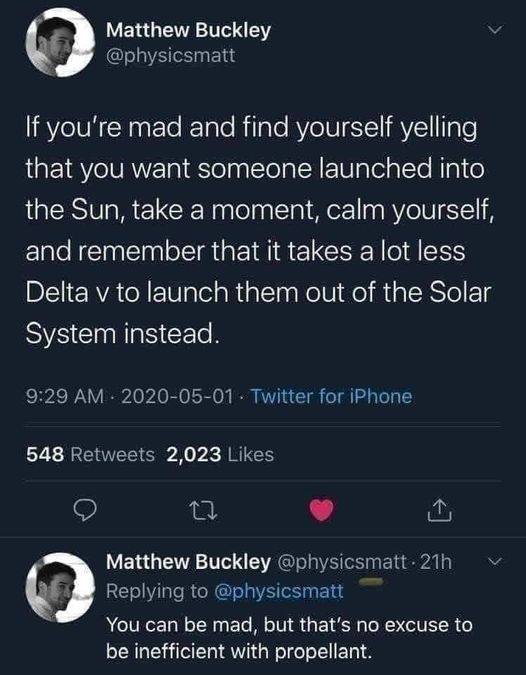
Good question, but if you cancel out only a little bit of orbital velocity, you just orbit in a little bit closer. Without any appreciable drag acting on you, there's nothing that will keep your orbit decaying. You'll just be in a smaller, perhaps slightly more eccentric orbit.
But you'd need a higher velocity to orbit closer...
Yeah, orbital mechanics gets a little bit mind-bendy sometimes. If you're in a stable circular orbit, accelerating in the direction you're traveling will actually result in you traveling more slowly because you have moved to a higher orbit, and firing engines to slow down will actually speed you up because you move in closer to the host body and take up a faster orbit.
This is actually a problem spacecraft deal with regularly. If a Dragon capsule is behind the ISS and wants to dock, using its thrusters to accelerate toward the ISS will actually result in it falling further behind. Decelerating will get it closer, though it will then be in a lower orbit. Orbital rendezvous is tough.